Neurofeedback: Retraining Your Brain for Optimal Performance
Can you imagine using the power of your mind to improve your mental health, cognitive abilities, and overall well-being? Welcome to the world of neurofeedback, a groundbreaking technique that's revolutionizing how we approach brain health and performance optimization. This cutting-edge therapy offers a unique way to tap into your brain's potential, promising benefits that range from stress reduction to enhanced focus and creativity.
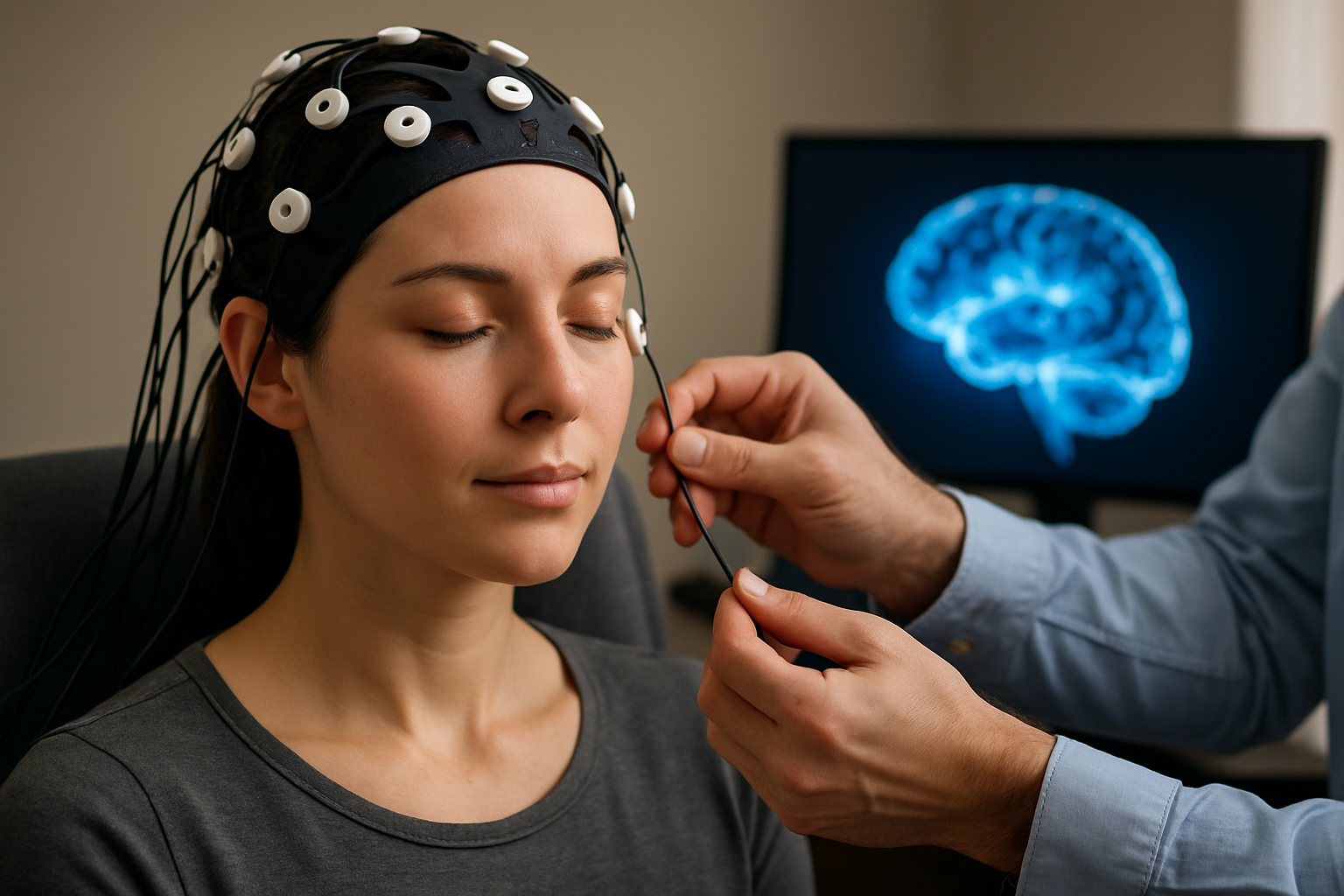
The concept of neurofeedback dates back to the 1960s when researchers discovered that people could learn to control their brain waves when given visual or auditory feedback. Since then, advancements in technology and neuroscience have significantly enhanced our understanding of brain plasticity and the potential for targeted brain training.
How Neurofeedback Works
During a neurofeedback session, sensors are placed on the scalp to measure electrical activity in specific areas of the brain. This activity is then translated into visual or auditory feedback, often in the form of a video game or animation. When the brain produces the desired wave patterns, the game progresses or a pleasant tone is heard. Conversely, when undesirable patterns are detected, the game may pause or the tone may change.
Through repeated sessions, the brain learns to produce more of the desired wave patterns, leading to improved function in targeted areas. This process is based on operant conditioning, where the brain is rewarded for producing specific patterns of activity, gradually reinforcing these patterns over time.
Applications and Benefits
Neurofeedback has shown promise in treating a wide range of conditions and enhancing various aspects of cognitive performance:
-
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of neurofeedback in improving attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity in individuals with ADHD.
-
Anxiety and Depression: By training the brain to produce more alpha waves associated with relaxation, neurofeedback can help alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression.
-
Sleep Disorders: Neurofeedback can help regulate sleep patterns by targeting brain wave frequencies associated with restful sleep.
-
Peak Performance: Athletes, executives, and artists are increasingly turning to neurofeedback to enhance focus, creativity, and overall cognitive performance.
-
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Emerging research suggests that neurofeedback may be effective in reducing symptoms of PTSD by helping individuals regulate their emotional responses.
The Neurofeedback Experience
A typical neurofeedback training program consists of multiple sessions, usually ranging from 20 to 40 sessions, depending on the individual’s goals and progress. Each session lasts about 30 to 60 minutes and is typically conducted once or twice a week.
During a session, the individual sits comfortably while sensors are attached to their scalp. They then engage in a task, such as watching a video or playing a game, which responds to their brain activity. The process is painless and non-invasive, making it suitable for people of all ages, including children.
Many individuals report feeling more relaxed and focused after neurofeedback sessions. However, it’s important to note that the effects of neurofeedback are cumulative, and significant improvements are typically observed after multiple sessions.
Challenges and Considerations
While neurofeedback shows great promise, it’s not without its challenges:
-
Cost: Neurofeedback sessions can be expensive and are not always covered by insurance.
-
Time Commitment: Achieving significant results often requires multiple sessions over several weeks or months.
-
Variability in Results: As with many therapies, individual responses to neurofeedback can vary.
-
Lack of Standardization: There is currently no standardized protocol for neurofeedback, which can lead to variations in treatment approaches and outcomes.
The Future of Neurofeedback
As technology advances, the future of neurofeedback looks increasingly promising. Researchers are exploring ways to make neurofeedback more accessible and effective:
-
Home-Based Systems: Development of user-friendly, at-home neurofeedback devices could make the therapy more affordable and convenient.
-
Integration with Virtual Reality: Combining neurofeedback with virtual reality environments may enhance engagement and effectiveness.
-
Personalized Protocols: Advances in AI and machine learning could lead to more personalized and targeted neurofeedback protocols.
-
Combination Therapies: Integrating neurofeedback with other therapies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy, may yield synergistic benefits.
Brainwave Basics: Understanding Your Mind’s Frequencies
-
Delta waves (0.5-4 Hz): Associated with deep sleep and restorative processes
-
Theta waves (4-8 Hz): Linked to creativity, intuition, and deep relaxation
-
Alpha waves (8-12 Hz): Indicative of a relaxed, alert state
-
Beta waves (12-30 Hz): Connected to active thinking and focus
-
Gamma waves (30-100 Hz): Associated with high-level information processing and cognitive performance
As we continue to unravel the mysteries of the human brain, neurofeedback stands out as a powerful tool for harnessing our innate neuroplasticity. By providing a direct interface between our conscious efforts and the underlying patterns of our brain activity, this innovative technique offers a unique pathway to improved mental health and cognitive performance. While more research is needed to fully understand its potential and limitations, neurofeedback represents an exciting frontier in our quest for optimal brain function and well-being.





